






|

|


|

|

DTS - Optical fiber distributed temperature sensoring systems (DTS)

DTS is a system in which the optical fiber itself serves as the sensor, measuring the continuous
thermal distribution along its length, so that it can monitor heat generation and detect fire over wide areas.
It can measure temperature distribution over a distance of up to 8km, at prices far lower than could be achieved by conventional
methods.



|

|

|

|


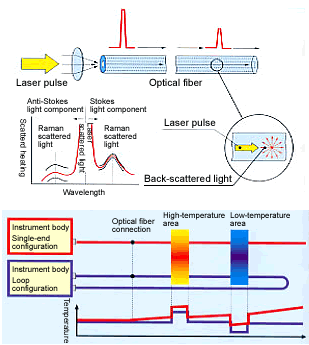
The measurement principle is based on the intrinsic temperature dependant nature of Raman scattering
generated when a laser pulse launched into the optical fiber, propagates along the optical fiber.
The Raman scattering is split into two bands of Stokes and Anti-Stokes roughly symmetrical about the incident laser pulse
wavelength.
Where the band of Anti-Stokes(shorter wavelrngths) exhibits a distinct temperature sensitivity and the band of Stokes(longer
wavelength) is weakly temperature sensitive.
Monitoring the back scatter of Anti-Stokes and Stokes by using OTDR(Optical Time Domain Reflectmetory) technology allows
distributed temperature sensing, since their intensities are dependent on the fiber temperature.
In practice, the ratio of Anti-Stokes to Stokes Light intensities is used for distributed temperature measurement to obtain the absolute temperature. Because the ratio is not affected by bend loss, splice loss, or connection loss. 

The measurement accuracy of the optical fiber DTS using Raman scattering is badly affected
with the fiber attenuation fluctuation along the fiber length.
The attenuation might be changed in high temperature beyond 350 °C, or low temperature below -200°C, and also be discontinuous
at splicing, connecting, and bending points.
However, the loop measurement configuration, in which the laser pulses are injected into the fiber cable alternately from
both ends, can resolve these difficulties by automatic cancellation of the cable attenuation effect.

Even if the optical fiber in a loop configuration breaks, a fiber breakage alarm is output,
and the system automatically switches to single-end measurement from both sides, so that it can continue measuring.


A built-in CPU processes temperature measurement, error judgment, self diagnosis and other
functions, so no external PC is required for normal monitoring.
The system starts working when the power is turned on so recovery from a power interruption is very simple.


The optical fiber can be divided into any desired length and, in the case of fire detection
modules, assigned up to 800 different zone settings.
Individual alarms can be set for each zone and multiple settings can be superimposed.


Laser power and light sensor sensitivity are constantly monitored and an alarm is issued if
their performance degrades below certain levels.


|

|

|

|



